Data governance plan is a critical element in any organization’s data management strategy. It outlines the policies, procedures, and guidelines for managing the collection, storage, use, and sharing of data across the enterprise. Data governance plan is designed to ensure data accuracy, consistency, security, privacy, and regulatory compliance. At Yeuesports, we discuss the importance of data governance plan, its key components, and how to develop an effective data governance plan for your organization.
Importance of Data Governance Plan
Data is one of the most valuable assets of any organization, and data governance plan is critical to ensuring that data is properly managed, protected, and utilized. An effective data governance plan helps to reduce risks associated with data, such as data breaches, data inaccuracies, and regulatory non-compliance. It also helps to ensure that data is used appropriately, which helps to build trust and credibility with stakeholders, customers, and regulators.
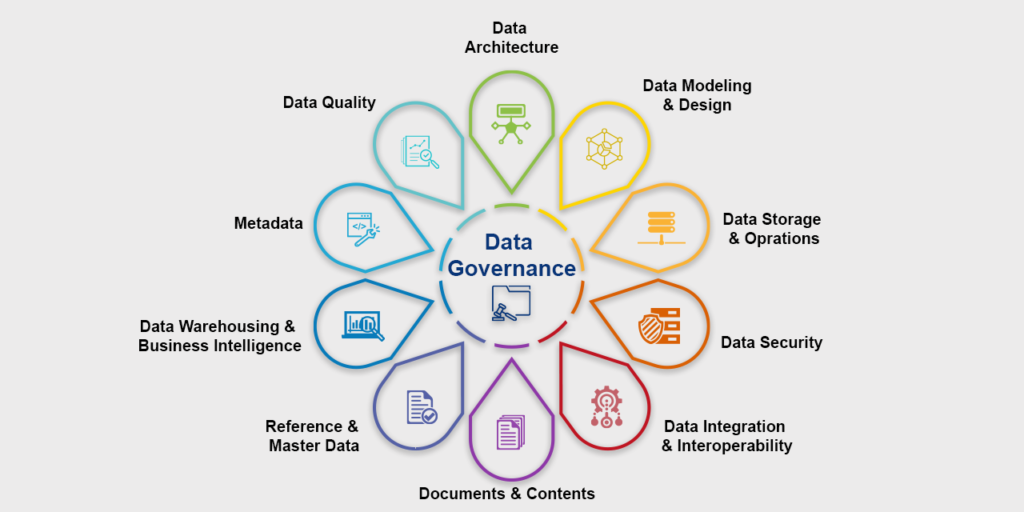
Key Components of Data Governance Plan
A data governance plan should include the following key components:
- Data Governance Policies: Data governance policies provide clear guidelines for managing data in the organization. These policies define the rules for data collection, storage, analysis, and sharing across the organization. They ensure that data is used appropriately and ethically, and they align with the organization’s overall goals and objectives. Examples of data governance policies include data classification policies, data retention policies, and data access policies.
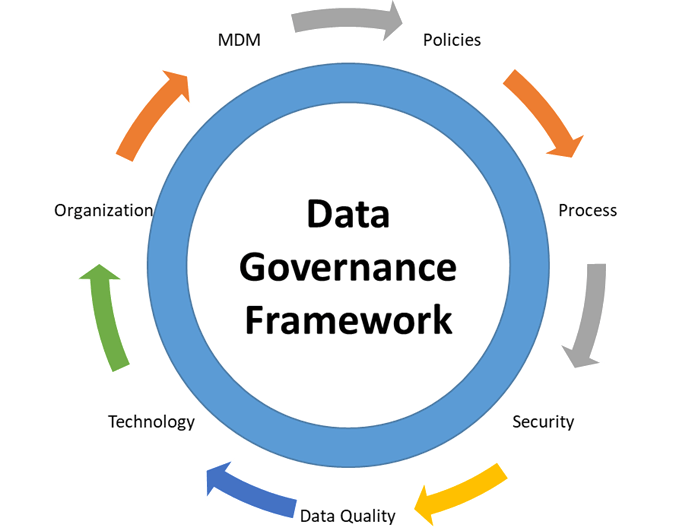
- Data Governance Framework: The data governance framework outlines the roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing data in the organization. It provides a structure for data governance and defines the decision-making process for data-related issues. The framework should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs and should include policies, procedures, and guidelines for data governance. Examples of data governance frameworks include the Data Management Body of Knowledge (DMBOK) and the Information Governance Reference Model (IGRM).
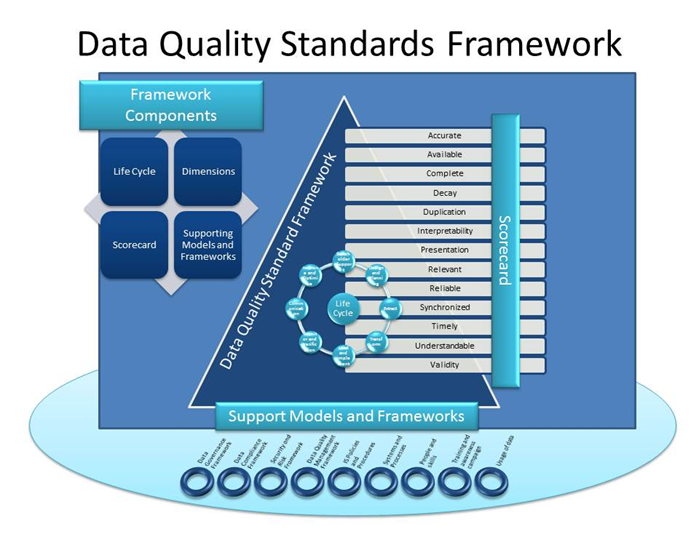
- Data Quality Standards: Data quality standards ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and reliable. These standards define the criteria for data quality, such as completeness, accuracy, timeliness, and consistency. They also provide guidelines for data validation, verification, and quality control. Examples of data quality standards include ISO 8000 and the Data Quality Assessment Framework (DQAF).
- Data Security and Privacy Measures: Data security and privacy measures protect data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. These measures ensure that data is kept confidential, secure, and protected from cyber threats. They also ensure that the organization complies with relevant data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Examples of data security and privacy measures include access controls, data encryption, and data anonymization.
- Data Management Tools: Data management tools enable effective data collection, storage, and analysis. These tools include data management software, data warehouses, data analytics tools, and data visualization tools. They enable the organization to manage data more efficiently and effectively, making it easier to derive insights and make data-driven decisions.
Developing an Effective Data Governance Plan
Developing an effective data governance plan requires a collaborative effort between various stakeholders in the organization. The following are the key steps in developing an effective data governance plan:
- Identify Data Governance Objectives and Stakeholders: The first step in developing an effective data governance plan is to identify the objectives of the plan and the stakeholders involved in data governance. This includes identifying the business goals and objectives that the data governance plan should support and the stakeholders who will be responsible for implementing the plan.
- Define Data Governance Policies: Once the objectives and stakeholders have been identified, the next step is to define the data governance policies. These policies should be aligned with the organization’s overall goals and objectives and should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs. They should provide clear guidelines for managing data across the organization and ensure that data is used appropriately and ethically.
- Develop Data Governance Framework: The data governance framework outlines the roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing data in the organization. This framework should be developed in collaboration with the stakeholders and should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs. It should provide a structure for data governance and define the decision-making process for data-related issues.
- Establish Data Quality Standards: Data quality standards ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and reliable. These standards define the criteria for data quality, such as completeness, accuracy, timeliness, and consistency. They also provide guidelines for data validation, verification, and quality control. The standards should be developed in collaboration with the stakeholders and should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs.
- Implement Data Security and Privacy Measures: Data security and privacy measures protect data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. These measures ensure that data is kept confidential, secure, and protected from cyber threats. They also ensure that the organization complies with relevant data protection regulations. The measures should be developed in collaboration with the stakeholders and should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs.
- Select Data Management Tools: Data management tools enable effective cloud data collection, storage, and analysis. These tools include data management software, data warehouses, data analytics tools, and data visualization tools. The tools should be selected based on the organization’s specific needs and should be integrated with the data governance framework.
- Implement and Monitor Data Governance Plan: Once the data governance plan has been developed, it should be implemented and monitored to ensure that it is effective and efficient. This includes communicating the plan to all stakeholders, providing training on the policies and procedures, and establishing metrics to monitor the effectiveness of the plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data governance plan is a critical element in any organization’s data management strategy. It helps to reduce risks associated with data, ensure data accuracy, consistency, security, privacy, and regulatory compliance. Developing an effective data governance plan requires a collaborative effort between various stakeholders in the organization, and it is essential for organizations to implement a robust data governance plan to protect their data assets and build trust with stakeholders, customers, and regulators.