Data governance is the process of managing and controlling data in an organization. The goal of data governance is to ensure the quality, consistency, security, and availability of data across the organization. A data governance plan is a comprehensive set of policies, procedures, and guidelines that are designed to manage data effectively. This article will discuss the importance of a data governance plan, key elements and steps to create.
Importance of a Data Governance Plan
In today’s digital world, organizations are generating large volumes of data every day. The data may come from different sources, such as customer transactions, social media, sensors, and other devices. The data may be stored in different formats, such as structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. Managing this data effectively is critical for the success of the organization. A data governance plan helps organizations to:

- Ensure data quality: A plan defines data quality standards and ensures that data is accurate, complete, and consistent. This is essential for making informed business decisions based on reliable data.
- Increase data security: A data governance plan includes policies and procedures to ensure data security. This helps to protect the organization’s data from cyber threats, data breaches, and other security risks.
- Ensure compliance: A plan ensures that the organization complies with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This is critical for avoiding legal and financial penalties and protecting the organization’s reputation.
- Improve data management: A data governance plan provides a framework for managing data effectively. This helps to reduce data duplication, improve data sharing, and optimize data storage.
Key Elements of a Data Governance Plan
A data governance plan typically includes the following key elements:
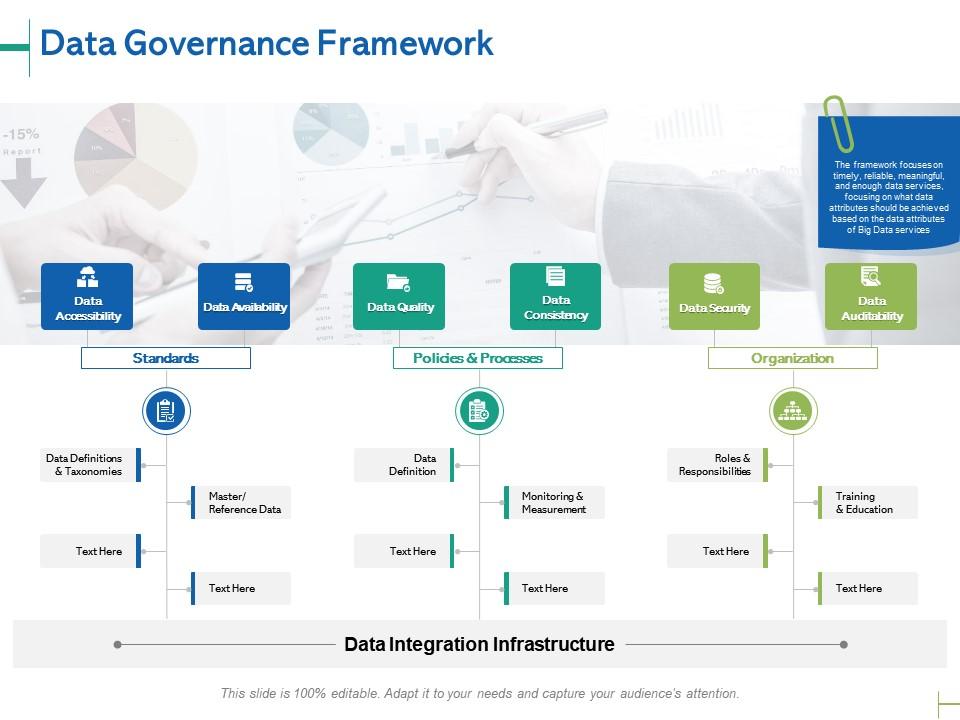
- Data Governance Framework: A data governance framework defines the organizational structure, roles, and responsibilities for data governance. This includes the data governance committee, data owners, data stewards, and other key stakeholders.
- Data Quality Standards: Data quality standards define the criteria for measuring data quality. This includes data accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, and relevancy.
- Data Security Policies: Data security policies define the procedures for securing data. This includes access control, data encryption, backup and recovery, and disaster recovery.
- Data Privacy Policies: Data privacy policies define the procedures for protecting sensitive data. This includes data anonymization, data masking, and data classification.
- Data Retention Policies: Data retention policies define the procedures for storing and disposing of data. This includes data archiving, data deletion, and data backup.
- Data Classification: Data classification defines the categorization of data based on its sensitivity, value, and criticality. This helps to determine the appropriate level of security, access control, and retention for each type of data.
- Data Governance Processes: Data governance processes define the procedures for managing data throughout its lifecycle. This includes data acquisition, data integration, data validation, data transformation, data storage, data retrieval, and data analysis.
Steps to Create a Data Governance Plan
Creating a data governance plan requires careful planning, collaboration, and execution. The following are the key steps to create plan:
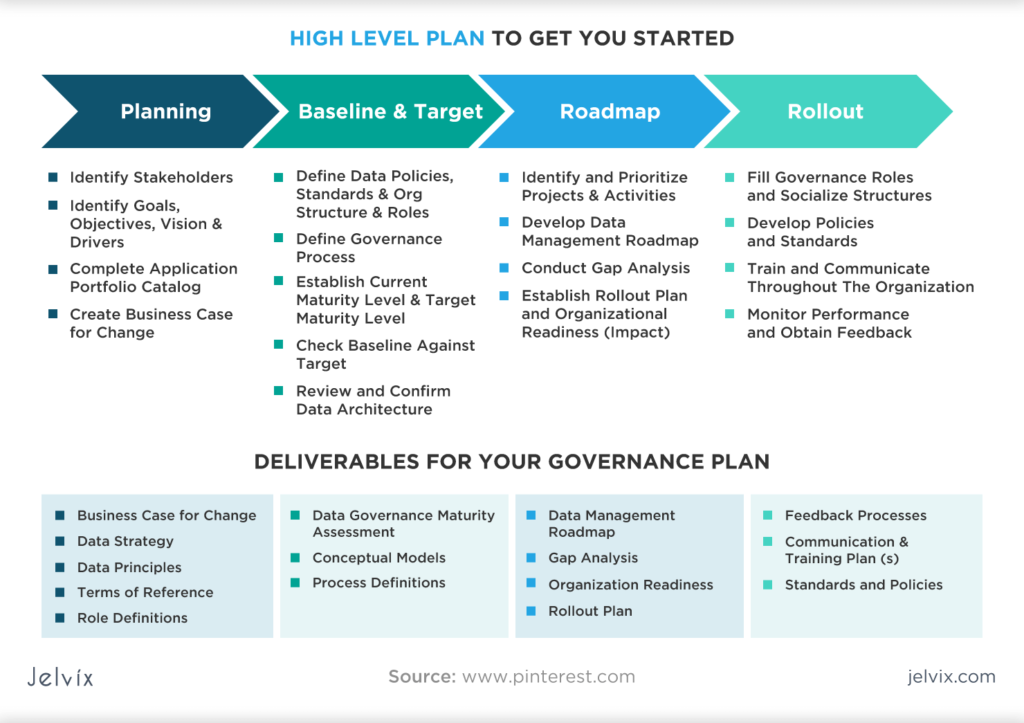
- Define the scope and objectives of the data governance plan: The first step is to define the scope and objectives of the data governance plan. This includes identifying the key stakeholders, data sources, data types, and business processes that are covered by the plan.
- Establish a data governance committee: The data governance committee is responsible for overseeing the development and implementation of the data governance plan. The committee should include representatives from different departments, such as IT, legal, compliance, and business.
- Identify data owners and data stewards: Data owners are responsible for the overall management of data within their respective domains. Data stewards are responsible for implementing the data governance policies and procedures within their domains. They are also responsible for ensuring that data quality standards are met.
- Define data quality standards: The next step is to define data quality standards based on the organization’s specific needs and requirements. This includes defining data accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, and relevancy.
- Define data security policies: Data security policies should be defined to ensure that data is protected from unauthorized access, theft, and misuse. This includes defining access control, data encryption, backup and recovery, and disaster recovery procedures.
- Define data privacy policies: Data privacy policies should be defined to ensure that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access and disclosure. This includes defining data anonymization, data masking, and data classification procedures.
- Define data retention policies: Data retention policies should be defined to ensure that data is stored for the appropriate period of time and disposed of properly. This includes defining data archiving, data deletion, and data backup procedures.
- Define data classification: Data classification should be defined to ensure that data is categorized based on its sensitivity, value, and criticality. This helps to determine the appropriate level of security, access control, and retention for each type of data.
- Implement data governance processes: Once the policies and procedures have been defined, the next step is to implement the data governance processes. This includes data acquisition, data integration, data validation, data transformation, data storage, data retrieval, and data analysis.
- Monitor and evaluate data governance plan: The final step is to monitor and evaluate the data governance plan to ensure that it is effective and efficient. This includes measuring data quality, data security, and data privacy metrics, as well as soliciting feedback from key stakeholders and making necessary adjustments to the plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a data governance plan is essential for managing data effectively in today’s digital world. It helps organizations to ensure data quality, increase data security, ensure compliance, and improve data management. A plan includes key elements such as a data governance framework, data quality standards, data security policies, data privacy policies, data retention policies, data classification, and data governance processes. Creating a data governance plan requires careful planning, collaboration, and execution, and should be monitored and evaluated regularly to ensure its effectiveness. By implementing a plan, organizations can maximize the value of their data assets and mitigate the risks associated with data management.
